In this blog we will delve into the treatment options and management strategies for Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Managing Parkinson’s requires a comprehensive approach that includes medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and proper nutrition. Each person’s experience with PD is unique, and hence, the treatment plan should be tailored to suit individual needs and symptoms.
Medications for Parkinson’s Disease
Introduction to Parkinson’s Disease Medications

There is a range of medications available for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. These medications aim to manage the symptoms, mainly by increasing the levels of dopamine or mimicking its effects in the brain, as the loss of dopamine-producing cells is a characteristic feature of PD.
Different Types of Medication and Their Functions
Levodopa
It is one of the most effective medications for treating PD. Once in the brain, levodopa is converted into dopamine. It is often combined with carbidopa (in a formulation known as Sinemet) which prevents levodopa from breaking down in the bloodstream before it reaches the brain.
Dopamine agonists
These medications mimic dopamine effects in the brain. Examples include pramipexole (Mirapex) and ropinirole (Requip). They are usually prescribed to individuals as a first line of treatment because it helps decrease the risk of motor complication development and may have a neuroprotective effect.
MAO-B inhibitors
These help to prevent the breakdown of dopamine in the brain by inhibiting the brain enzyme monoamine oxidase B (MAO B), which metabolizes dopamine. These include medications such as selegiline and rasagiline, that are known to improve several PD movement symptoms.
Anticholinergic medications
These were some of the first medications used to treat PD and are effective primarily for controlling tremor. These medications reduce tremor by blocking acetylcholine, a brain chemical that influences movement. Older individuals are especially susceptible to confusion and hallucinations when using anticholinergics and so these mediactions are not recommended for people over the age of 70.
Side-effects and Considerations when Using Medications
As with any medications, those for PD also come with potential side effects, which may include nausea, dizziness, and sleep disturbances. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to find a balance between the benefits and side effects.
Advanced Treatments for Parkinson’s Disease
Overview of Advanced Treatments
When medication alone is not sufficient to manage the symptoms of PD, more advanced treatments may be considered.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS is a surgical procedure wherein electrodes are implanted in specific areas of the brain. These electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in the chest that sends electrical impulses to the brain, helping to alleviate PD symptoms.
Duopa Therapy
In this treatment, a combination of levodopa and carbidopa is directly delivered to the small intestine in a gel form through a surgically implanted tube, which helps in providing a more continuous delivery of medication.
Other Emerging Treatments
Research is ongoing, and new treatments such as gene therapy, stem cell therapy, and focused ultrasound are being investigated.
The Role of Physical Therapy and Exercise

Benefits of Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy and regular exercise can significantly improve the quality of life for people with PD. They can help with maintaining balance, strength, mobility, and flexibility.
Different Types of Exercises and Their Impacts
Aerobic Exercise
Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes a week can improve cardiovascular health, which is vital for overall well-being. Aerobic exercise also increases the release of dopamine, which can be beneficial in managing PD symptoms.
Resistance Training
This form of exercise involves lifting weights or using resistance bands. Resistance training strengthens muscles, which is essential in counteracting the muscle weakness typical in PD. It can also improve the ability to carry out daily activities such as lifting objects and climbing stairs.
Tai Chi, Yoga, and Pilates
These low-impact exercises focus on balance, flexibility, and breathing. For people with PD, these exercises can be very beneficial in improving postural stability, reducing the risk of falls, and relieving muscle rigidity. Moreover, the focus on breathing and mindfulness can have positive effects on mental health.
Tailoring a Physical Therapy Program
It is essential to individualize physical therapy programs to accommodate the patient’s current physical condition, the progression stage of the disease, and personal goals. Consulting with a physical therapist who has experience in neurology or working with PD patients can help develop an effective and personalized program.
Dietary Considerations for Parkinson’s Disease
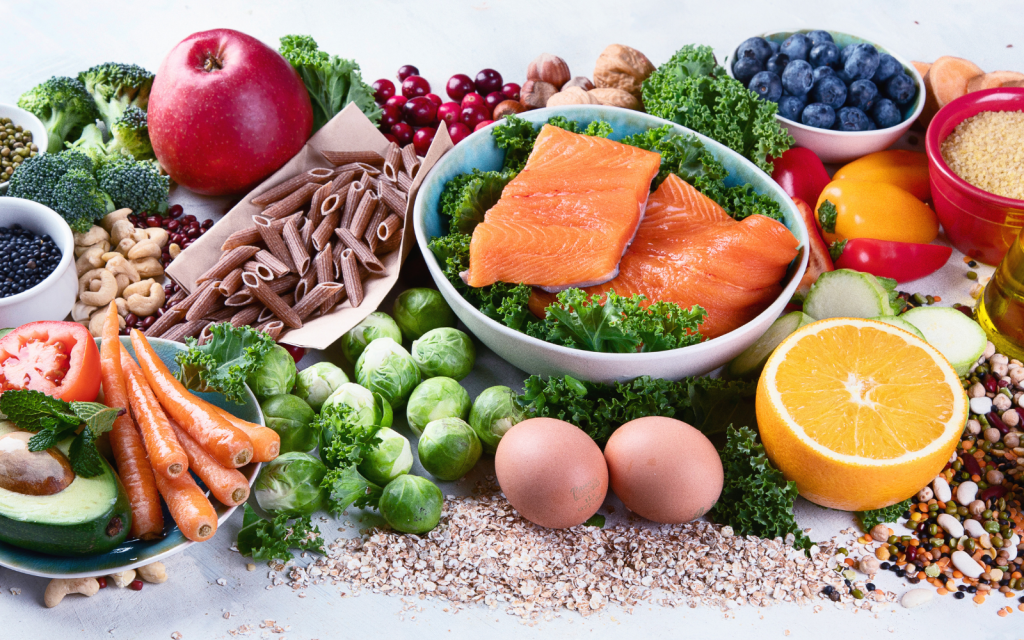

The Impact of Diet on Parkinson’s Disease
Diet can play a critical role in managing PD. Eating a balanced diet not only helps in maintaining overall health but can also alleviate some symptoms of PD.
Foods to Include in the Diet
Antioxidant-rich foods
Incorporating foods like berries, dark chocolate, nuts, and vegetables can help combat oxidative stress, which is believed to play a role in PD.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can be neuroprotective.
Foods to Avoid with Parkinson’s Disease
High protein meals
It is advised to consume proteins in moderation especially around the time of taking levodopa, as proteins can interfere with the absorption of this medication.
Processed foods and sugary drinks
They can aggravate PD symptoms and negatively impact overall health. It is advisable to minimize the intake of these foods.
Lifestyle Modifications to Manage Parkinson’s Disease

Importance of Lifestyle Changes
Implementing lifestyle changes is critical in managing PD. This includes physical activity, dietary adjustments, mental health management, and engaging in social activities.
Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
Managing stress is crucial for patients with PD as stress can worsen symptoms. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can be very effective in managing stress levels.
Sleep Hygiene and Importance of Rest
Ensuring good sleep quality is essential for brain health and managing the symptoms of PD. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable and quiet sleeping environment, and avoiding stimulants close to bedtime can improve sleep quality.
Social Engagement and Support
Staying socially engaged through participation in community activities or joining support groups is vital. Social support can alleviate feelings of isolation and depression and has a positive impact on the mental health of individuals living with PD.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing Parkinson’s Disease is multi-faceted. Through a combination of medication, physical therapy, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications, it’s possible to manage symptoms and maintain a higher quality of life. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to tailor the management plan to individual needs.

In your journey as a caregiver for a loved one, it’s essential to explore various resources and tools that can help enhance their overall well-being. One such valuable product is SilverPad by SilverActivities, a senior-friendly tablet with large buttons and text designed specifically for seniors. It offers a range of engaging games and activities that stimulate cognitive functions, providing mental stimulation and enjoyment for seniors. Trusted by many senior care institutions and therapists, SilverPad has proven to be an effective tool for promoting cognitive health and maintaining a sense of engagement and connection.

